Continuous Casting Machine
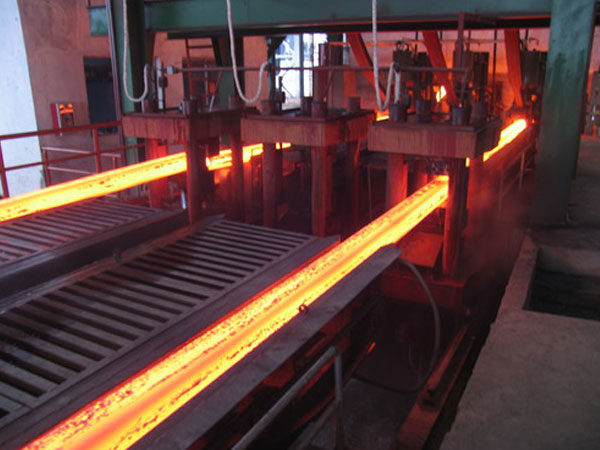

Ability to cast regular shapes and certain irregular configurations in long tubular form, which is difficult for other casting methods.
Continuous cast bars require appreciably less machining stock.
Continuous cast material is consistently dense and homogeneous in structure, and therefore well-suited for pressure applications.
Straight, true, and concentric product for high speed bar machines.
Many suppliers maintain stock sizes for ready availability to distributors and others requiring full lengths.
If the shape is optimized, the clean-up stock required on continuous cast material is often less than that needed for parts produced with other casting processes. Stock of 1/32 to 3/32 inches per side depending on the casting size is normally adequate.
Continuous castings have an inherent advantage in mechanical properties over other methods because of the chilling and the excellent feeding of molten metal during solidification.
Continuous castings perform well under pressure.
Fume Extraction System
Dusty fumes exhausted from induction furnace at high temperature (120 deg. C) and gas volume around 1,73,000 m3/hr. These fumes were captured by side draft hood having the inbuilt Axial flow fan for effective local suction draft which helps to reduce the work zone emissions. A Swiveling mechanism has been provided to take away the hood from one furnace (Working) and other furnace (Stand by) and for easy loading and unloading operation of charge. Spark arrestor provided before the bag filter to arrest the spark if any which travel along with the fume gases. Primary fumes first pass through spark arrestor and then connected to specially designed Rieco Bag House and clean gas will pass to atmosphere through exhaust Stack.
Electric ARC Furnace
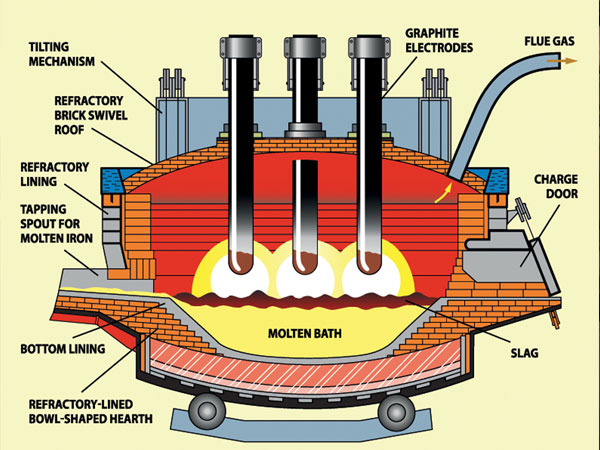
The working of electric furnace includes charging the electrode, meltdown period (melting the metal) and refining. The heavy and light scrap in the large basket is preheated with the help of exhaust gas. For speeding up the slag formation, burnt lime and spar are added to it. The charging of furnace takes place by swinging the roof of the furnace. As per requirement, the hot metal charging also takes place. Next is the meltdown period. The electrodes are moved down onto the scrap in this period. Then the arc is produced between the electrode and metal. By considering the protection aspect, low voltage is selected for this. After the arc is shielded by electrodes, the voltage is increased for speeding up the melting process. In this process, carbon, silicon, and manganese get oxidized. The lower current is required for large arc production. The heat loss is also less in this. Melting down process can be fastening by deep bathing of electrodes.
Refining process starts during melting. The removal of sulfur is not essential for single oxidizing slag practice. Only phosphorous removal is required in this. But in double slag practice, both (S and P) are to be removed. After the deoxidizing; in double slag practice, the removal of oxidizing slag is performed. Next, with the help of aluminum or ferromanganese or ferrosilicon, it gets deoxidized. When the bathing chemistry and required temperature is reached, the heat will get deoxidized. Then, the molten metal is ready for tapping. For the cooling of the furnace, tubular pressure panels or hollow annulus spraying can be used.
Address
23B, NS Road Kolkata
Contact
info@gleambusiness.com
+91-9681033767

 Linkedin
Linkedin Facebook
Facebook Youtube
Youtube